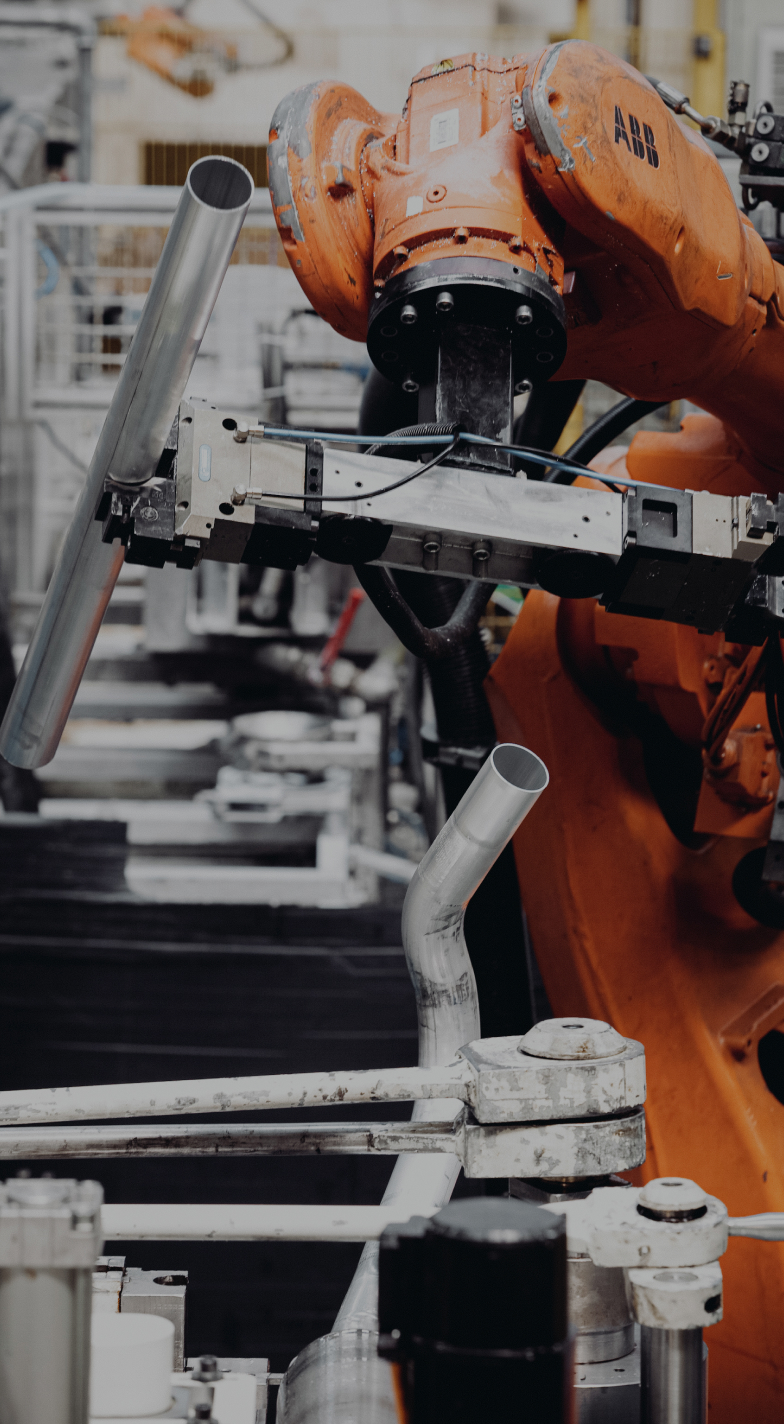
Metal forming vs. die-cast
In general, metal forming is a good choice for parts that are relatively simple and do not require a high degree of precision. Die casting is a good choice for parts that are more complex and require a high degree of precision. We strongly focus on CO2 reduction and improving your production processes.
Metal forming and die casting are both manufacturing processes used to create metal parts. However, there are some key differences between the two processes.
CO2 savings
Metal forming has various benefits vs die-casting:
CO2 savings and the CO2 footprint of a product have a major influence on our parts life cycle. In order to reduce the CO2 footprint of die-cast parts and at the same time achieve cost savings, we rely on single or multi-layer forming.
- Up to 50% weight advantage
- Cost advantge up to 25%
- Noise and thermal shielding advantages
Check out our metalworking capabilities. Contact us today!
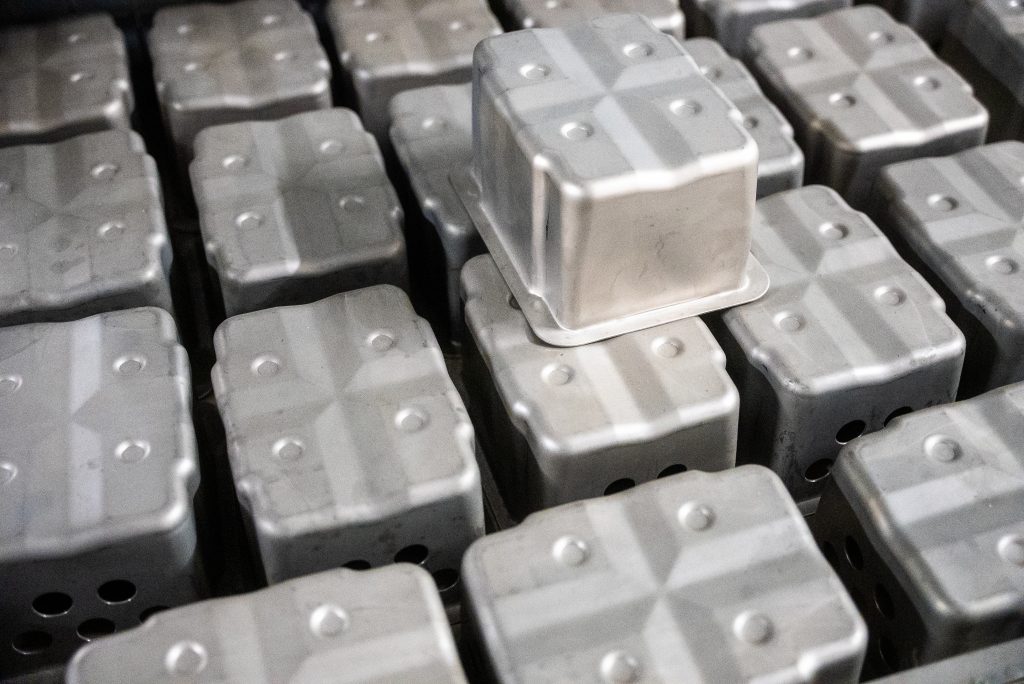

Materials
Some metals, like aluminum and certain steel alloys, are highly formable and ideal for a wide range of metal forming processes.
- Stainless steel
- High strenght steel
- Titanium
- Aluminium Alloys
Metal forming often reduces CO2 emissions compared to die casting due to its lower energy consumption and potential for material reuse. Contact us to work together on a greener future!
Our mission:
Optimized production
We optimize your processes. Costs are reduced. We are driven by quality and individuality.
Create value
Creating complex solutions for our customers is the most important thing for us – simply our core competence.
Metal forming FAQs
Deep drawing shapes everything from car hoods to beverage cans. It excels at complex shapes, but there’s a limit. Deep drawn parts typically have rounded bottoms and can’t have sharp corners or deep undercuts.
Deep drawing is generally cheaper for complex, high-volume parts. Stamping is best for simple, high-volume parts. Welding offers more flexibility in materials but can be expensive for complex shapes, especially for large quantities.
Deep drawing typically works best with thin to medium-thickness sheet metal. There’s a separate process called tube drawing for tubes. Material-wise, it works well with ductile metals like aluminum or copper, but may not be suitable for very hard or brittle ones.